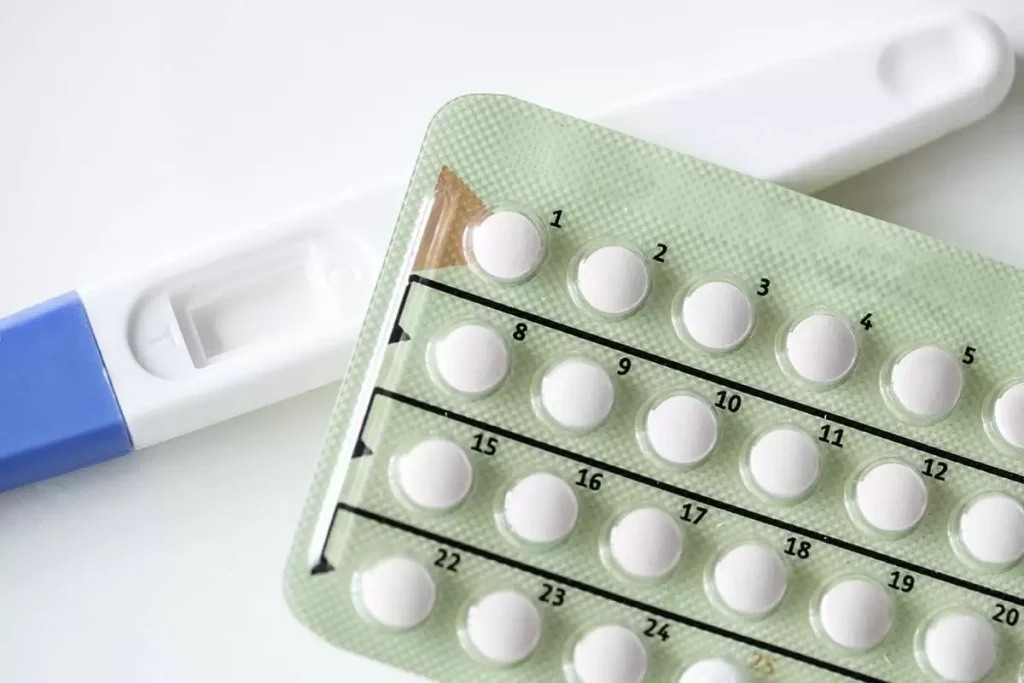
Oral contraceptive pills are one of the most popular and effective methods for managing reproductive health. They offer a convenient way to prevent pregnancy while providing additional benefits, such as regulating menstrual cycles, reducing cramps, and supporting hormonal balance. However, to get the most out of these pills, it’s important to understand the different types, how they work, proper usage, and potential side effects. This guide breaks down everything you need to know to make informed choices and use oral contraceptives safely and effectively.
What Are Oral Contraceptive Pills?
Oral contraceptive pills are medications containing hormones that prevent pregnancy. They are safe, affordable, and highly effective when taken consistently at the same time every day. Aside from contraception, some pills also provide additional health benefits, such as regulating periods, reducing menstrual cramps, and improving acne.
Types Of Pills
1. Combination
Combination pills contain both estrogen and progestin, which work together to prevent ovulation and pregnancy. A typical monthly pack usually has three consecutive weeks of hormone-containing pills, followed by a week of placebo (hormone-free) or iron tablets that trigger your period.
These pills are commonly chosen by women who prefer a reliable daily contraceptive method and also benefit from hormone-related effects, like lighter or more predictable periods.
2. Progestin-Lamang
Progestin-only pills are also sometimes called the mini-pill because of their small size. They don’t contain estrogen, and are often given to women who are sensitive to combination pills or are experiencing side effects because of them, and to breastfeeding mothers who need contraception. Progestin-only pills release a small amount of progestin every day for a month (28 pills), and will not induce your period on a set week. If used correctly, less than one woman out of 100 will get pregnant in a year. With typical use, the pill is 91% effective.
Ang pagkabigo o hindi wastong paggamit ang mga pangunahing dahilan kung bakit nawawala ang bisa ng mga tabletas. Ang paglimot sa pag-inom ng mga tabletas, pagkawala ng pakete, pagkabigo sa pagbili ng bagong pakete—ito ang ilan sa mga karaniwang pagkakamali sa mga tabletas na maaaring humantong sa pagbubuntis. Bago magpasya na gumamit ng mga tabletas, makabubuting isaalang-alang muna ang mga bagay na ito. Narito ang ilang mga paraan upang matulungan kang matandaan na uminom ng iyong mga tabletas araw-araw:
- Panatilihin ang isang kalendaryo upang makita kung kailan mo kailangang magsimula ng bagong pack.
- Magtakda ng alarm sa iyong telepono sa pare-parehong oras araw-araw.
- Ipares ang pag-inom ng iyong tableta sa isa pang aktibidad na ginagawa mo araw-araw sa parehong oras, tulad ng pagsisipilyo ng iyong ngipin o pagkain ng almusal.
How Oral Contraceptive Pills Work
The hormones in the pills—estrogen and progestin—prevent pregnancy in two main ways:
Thickening cervical mucus: Progestin makes it harder for sperm to reach the egg, providing an additional barrier to fertilization.
Preventing ovulation: Estrogen stops the release of an egg, so sperm has nothing to fertilize.
How to Use Oral Contraceptive Pills
Ang pag-inom ng tableta ay walang problema, ngunit ang pag-alala na uminom ng iyong tableta sa halos parehong oras araw-araw, nasaan ka man o kung ano ang iyong ginagawa ay nangangailangan ng maraming pangako at pagkakapare-pareho. Tanungin ang iyong sarili: gaano ka nakatuon sa mga ganitong bagay?
Kung umiinom ka ng 28-araw na pill pack, uminom ng tableta araw-araw at magsimula sa isang bagong pack pagkatapos matapos ang nauna. Kung umiinom ka ng 21-day pill pack, uminom ng pill araw-araw sa loob ng 21 araw, pagkatapos ay susundan ng pitong araw na walang pills. Sa ika-28 araw, magsimula sa isang bagong pakete. Mahalagang huwag laktawan ang isang tableta sa mga araw na dapat kang uminom ng isa.
Ang iyong pagkamayabong at kakayahang magbuntis ay bumalik sa loob lamang ng ilang araw pagkatapos ihinto ang tableta, kaya naman mahalagang huwag laktawan ang isang tableta kung wala ka pang planong magbuntis, o gumamit ng ibang paraan ng proteksyon sa sandaling itigil mo ang tableta. .
Benefits of Oral Contraceptive Pills
- Easy to take—just swallow with water
- Hindi nakakaabala sa pakikipagtalik
- May make periods lighter
- Can let you control when to have your period
- Certain pills help clear up acne
- Can reduce menstrual cramps and PMS
- Maaaring makatulong ang ilang partikular na tableta na maiwasan ang ilang problema sa kalusugan gaya ng endometrial at ovarian cancer, anemia, ovarian cyst, at pelvic inflammatory disease.
Possible Side Effects
Some women experience mild side effects as their body adjusts to hormones. Most disappear after a few months:
- Bleeding between periods
- Sore breasts
- Nausea or vomiting
- Mood swings
Longer-lasting effects may include changes in libido.
Tip: If side effects are severe or persistent, consult your healthcare provider for guidance or alternative options.
Mga Karaniwang Hindi Pagkakaunawaan
- Dapat inumin araw-araw, nakipagtalik man o hindi ang isang babae sa araw na iyon para maging mabisa ang oral contraceptive pill.
- Hindi nakakagambala sa isang kasalukuyang pagbubuntis.
- Kung napalampas mo o nakalimutan mo ang isang tableta, ang pamamaraang ito ay maaaring hindi gaanong epektibo.
Conclusion
Oral contraceptive pills are a safe and effective way to manage reproductive health. By understanding the types of pills, how they work, and strategies to maintain consistency, you can make informed choices that fit your lifestyle and health needs.
Remember: Open communication with your healthcare provider is key to managing side effects and optimizing the pill’s benefits.
Pinagmulan:
Planned Parenthood. (nd). Gaano kabisa ang birth control pill? Planned Parenthood. Nakuha mula sa
https://www.plannedparenthood.org/learn/birth-control/birth-control-pill/how-effective-is-the-birth-control-pill