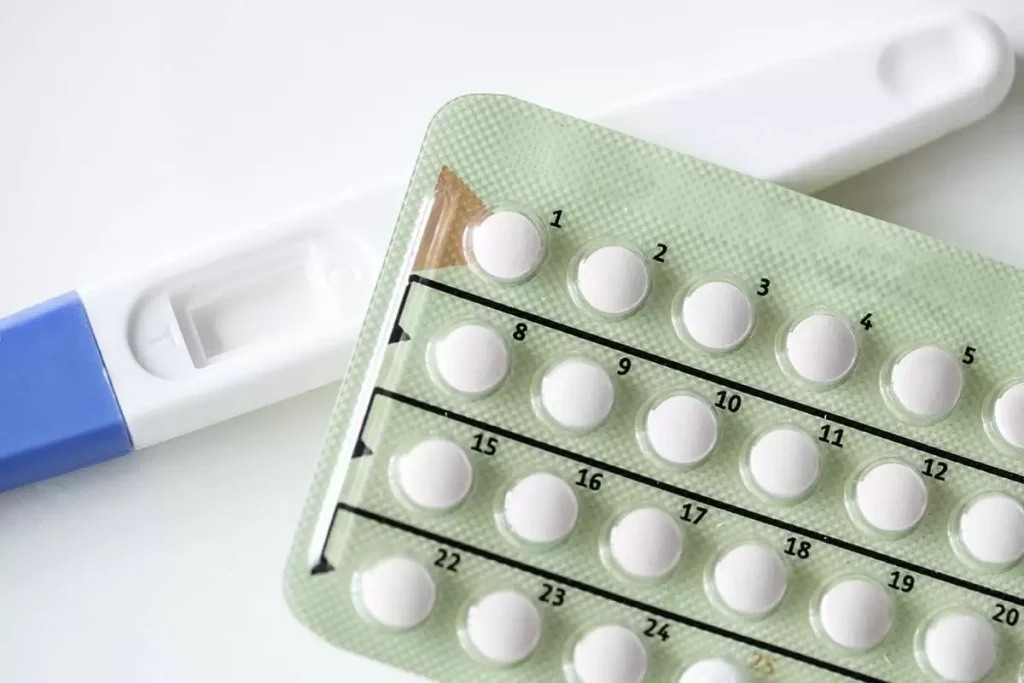
Oral contraceptive pills are one of the most popular and effective methods for managing reproductive health. They offer a convenient way to prevent pregnancy while providing additional benefits, such as regulating menstrual cycles, reducing cramps, and supporting hormonal balance. However, to get the most out of these pills, it’s important to understand the different types, how they work, proper usage, and potential side effects. This guide breaks down everything you need to know to make informed choices and use oral contraceptives safely and effectively.
What Are Oral Contraceptive Pills?
Oral contraceptive pills are medications containing hormones that prevent pregnancy. They are safe, affordable, and highly effective when taken consistently at the same time every day. Aside from contraception, some pills also provide additional health benefits, such as regulating periods, reducing menstrual cramps, and improving acne.
Types Of Pills
1. Combination
Combination pills contain both estrogen and progestin, which work together to prevent ovulation and pregnancy. A typical monthly pack usually has three consecutive weeks of hormone-containing pills, followed by a week of placebo (hormone-free) or iron tablets that trigger your period.
These pills are commonly chosen by women who prefer a reliable daily contraceptive method and also benefit from hormone-related effects, like lighter or more predictable periods.
2. Progestin-Only
Progestin-only pills are also sometimes called the mini-pill because of their small size. They don’t contain estrogen, and are often given to women who are sensitive to combination pills or are experiencing side effects because of them, and to breastfeeding mothers who need contraception. Progestin-only pills release a small amount of progestin every day for a month (28 pills), and will not induce your period on a set week. If used correctly, less than one woman out of 100 will get pregnant in a year. With typical use, the pill is 91% effective.
Messing up or failure to correctly use are the main reasons why pills lose their effectiveness. Forgetting to take the pills, losing the pack, failure to buy a new pack—these are some of the common mistakes with the pills that can lead to pregnancy. Before deciding to use the pills, it’s good to consider these things first. Here are some ways to help you remember to take your pills every day:
- Keep a calendar to see when you need to start a new pack.
- Set an alarm on your phone at a consistent time every day.
- Pair taking your pill with another activity you do every day at around the same time, such as brushing your teeth or eating breakfast.
How Oral Contraceptive Pills Work
The hormones in the pills—estrogen and progestin—prevent pregnancy in two main ways:
Thickening cervical mucus: Progestin makes it harder for sperm to reach the egg, providing an additional barrier to fertilization.
Preventing ovulation: Estrogen stops the release of an egg, so sperm has nothing to fertilize.
How to Use Oral Contraceptive Pills
Taking the pill is no problem, but remembering to take your pill at around the same time every day, no matter where you are or what you’re doing takes a lot of commitment and consistency. Ask yourself: how dedicated are with these kind of things?
If you’re taking the 28-day pill pack, take a pill every day and start with a new pack right after finishing the previous one. If you’re taking the 21-day pill pack, take a pill every day for 21 days, then followed by seven days with no pills. On the 28th day, start on a new pack. It’s important to not skip a pill on the days when you’re supposed to take one.
Your fertility and ability to get pregnant returns in just a few days after stopping the pill, that’s why it’s important to not skip a pill if you have no plans of getting pregnant yet, or use another method of protection as soon as you stop the pill.
Benefits of Oral Contraceptive Pills
- Easy to take—just swallow with water
- Doesn’t interrupt sex
- May make periods lighter
- Can let you control when to have your period
- Certain pills help clear up acne
- Can reduce menstrual cramps and PMS
- Certain pills may help prevent some health problems such as endometrial and ovarian cancer, anemia, ovarian cysts, and pelvic inflammatory disease.
Possible Side Effects
Some women experience mild side effects as their body adjusts to hormones. Most disappear after a few months:
- Bleeding between periods
- Sore breasts
- Nausea or vomiting
- Mood swings
Longer-lasting effects may include changes in libido.
Tip: If side effects are severe or persistent, consult your healthcare provider for guidance or alternative options.
Common Misunderstandings
- Must be taken every day, whether or not a woman had sex that day for oral contraceptive pills to be effective.
- Does not disrupt an existing pregnancy.
- If you miss or forget a pill, this method can be less effective.
Conclusion
Oral contraceptive pills are a safe and effective way to manage reproductive health. By understanding the types of pills, how they work, and strategies to maintain consistency, you can make informed choices that fit your lifestyle and health needs.
Remember: Open communication with your healthcare provider is key to managing side effects and optimizing the pill’s benefits.
Source:
Planned Parenthood. (n.d.). How effective is the birth control pill? Planned Parenthood. Retrieved from
https://www.plannedparenthood.org/learn/birth-control/birth-control-pill/how-effective-is-the-birth-control-pill