What is it?
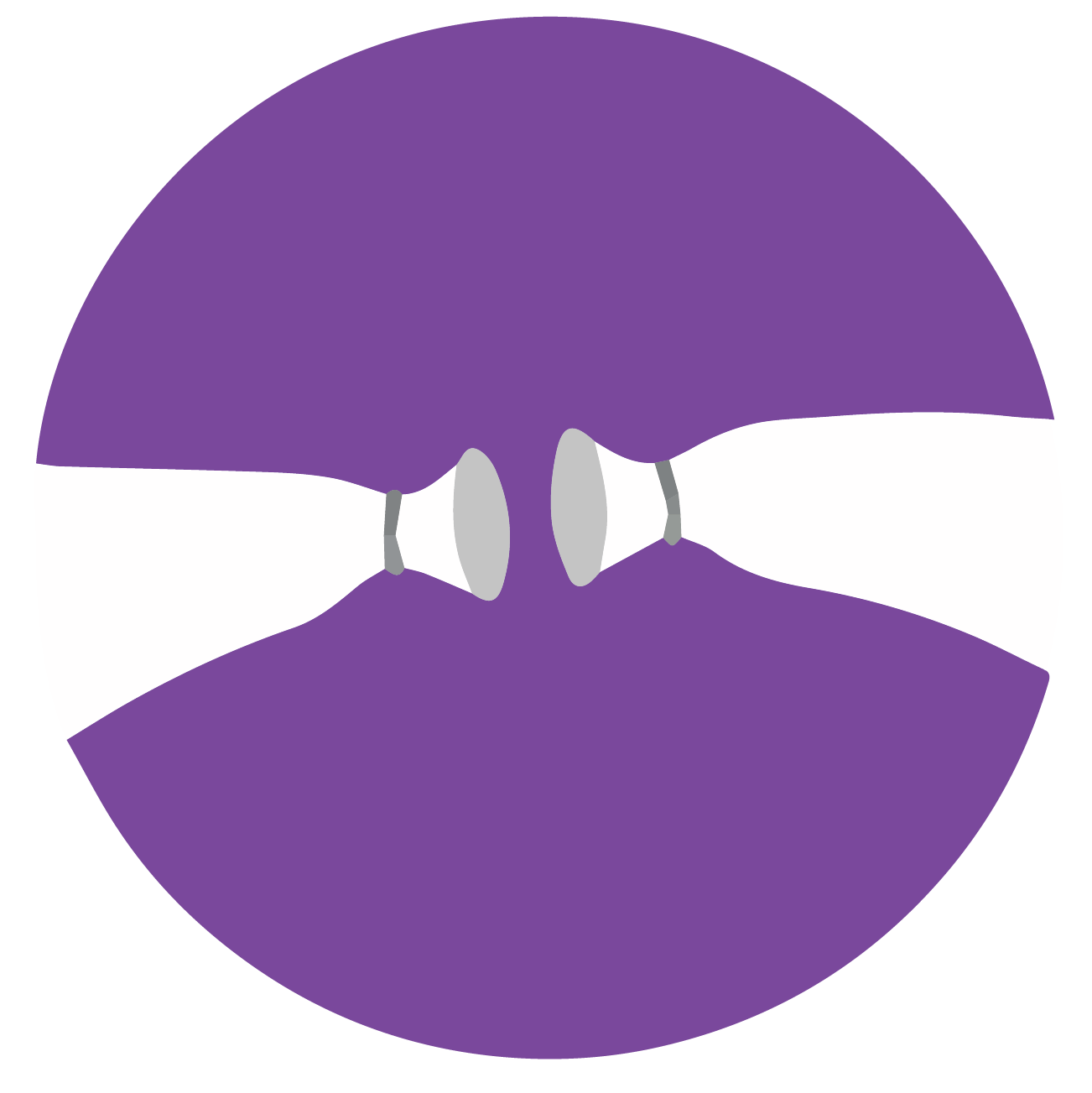
Bilateral tubal ligation (BTL), commonly known as ‘tubes tied,’ is a permanent form of female sterilization. It involves surgically closing or blocking both fallopian tubes, preventing eggs from traveling from the ovaries to the uterus and thus preventing pregnancy. BTL is a safe and highly effective option for women who are certain they do not want more children, offering a permanent solution with high success rates.
How does it work?
BTL is done with local anesthesia. A small incision is made near the navel. The fallopian tubes are then cut and the ends are tied or stitched. The incisions are closed with stitches.
How effective is the method?
The procedure is over 99% effective in preventing pregnancy. The failure rate is very low, with fewer than 1 in 200 women becoming pregnant after the procedure.
Pros
- Does not affect hormone levels or menstrual cycles
- Lowers the risk of ovarian cancer
Cons
- Reversal may be difficult and not always successful
- Surgical risks such as bleeding and infection
Myths and Misconceptions


DKT Philippines Foundation
Is the only outreach service in the Philippines offering free Bilateral Tubal Ligations (BTL) and comprehensive counseling on modern contraception, including pills, injectables, and condoms. Through partnerships with local government units (LGUs) and family planning organizations, we provide both facility-based and mobile clinic services to ensure that all Filipinos, regardless of location or socio-economic status, have access to high-quality family planning.
If interested to avail of the FREE BTL or bilateral tubal ligation, please message DKT Philippines Foundation on Facebook
Reference:
Family Planning Handbook. (n.d.). Chapter 12: Female sterilization. Retrieved August 22, 2024, from https://fphandbook.org/chapter-12-female-sterilization
Mayo Clinic. (n.d.). Tubal ligation: What you can expect. Retrieved August 27, 2024, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/tubal-ligation/about/pac-20388360
University of Utah Health. (n.d.). Tubal ligation: What to expect, effectiveness, & recovery. Retrieved August 27, 2024, from https://healthcare.utah.edu/womens-health/gynecology/surgery/tubal-ligation